General Building Data
Building Name - Health and Human Development Building
Location & Site - University Park, PA (The Pennsylvania State University)
Building Occupant Name - The College of Health and Human Development
Occupancy Type - Type B and Type A (Office, Classrooms, and Labs) [International Building Code]
Size - 150,000 SF
Number of Stories - 4 floors + Mechanical Penthouse
Dates of Construction - February 2013 - June 2015
Cost Information - Building Cost = $45 Million, Overall Project Cost = $59 Million
Project Delivery Method - Design-Bid-Build (DGS - Low bid project)
Project Team
Architecture
Architecture - The Health and Human Development Building is Phase 2 of The Penn State Henderson demolition and renovation project. The building was designed to blend in with the architectural facades and features of the surrounding buildings such as Old Main and the Biobehavioral Health Building. Penn State’s push to create an aesthetically pleasing view from College Avenue is also incorporated into this project. The building façade has been designed to match the surrounding buildings, which are composed mostly of Georgian style architecture. This type of architecture is composed of a large amount of hand-placed brick and limestone.
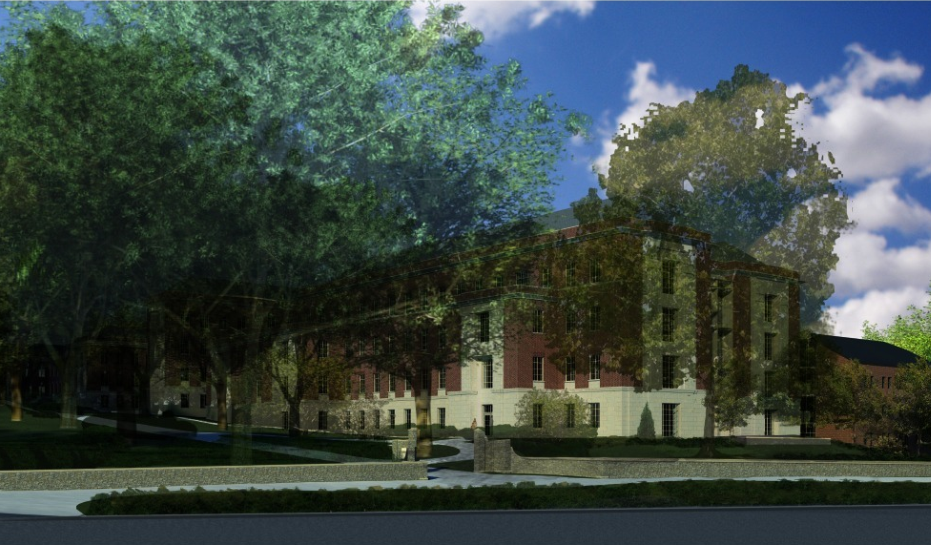 One of the main features of this project is the large atrium that faces College Avenue. This atrium will act as a transition space as well as a gathering place for students and faculty. The remaining of the building interior is composed of classrooms, offices, and labs, which will be utilized for students and faculty of the college of Health and Human Development. One of the main features of this project is the large atrium that faces College Avenue. This atrium will act as a transition space as well as a gathering place for students and faculty. The remaining of the building interior is composed of classrooms, offices, and labs, which will be utilized for students and faculty of the college of Health and Human Development.
Figure 1 Image Courtesy of BCJ
Code - The following codes are applicable for the construction of this project:
- The Pennsylvania Uniform Construction Code (UCC)
- 2006 Internation Building Code (IBC)
- 2006 International Plumbing Code (IPC)
Zoning
The zoning code in affect for this project is the State College Zoning Ordinance. The zoning district is the University Planned District (UPD) within subdistrict 5. There is a setback of a minimum 18 feet (measured from the curb) where the subdistrict adjoins College Avenue across non-University property in the Borough of State College zoned C. Maximum building height requirements for the University will also be met. Parking for this project shall meet the overall UPD parking plan developed by the University.
Historical Requirements
The building has been designed to match the architecture of the Henderson North Building, which was constructed in 1915. Old Main, Penn State’s building of uttermost signifcance, also plays the role of influence on this building.
Building Enclosure
The exterior of the building is composed of mainly masonry walls. The typical wall will be comprised of face brick that will be a molded colonial brick, which will complement the brick that was used for Phase One and 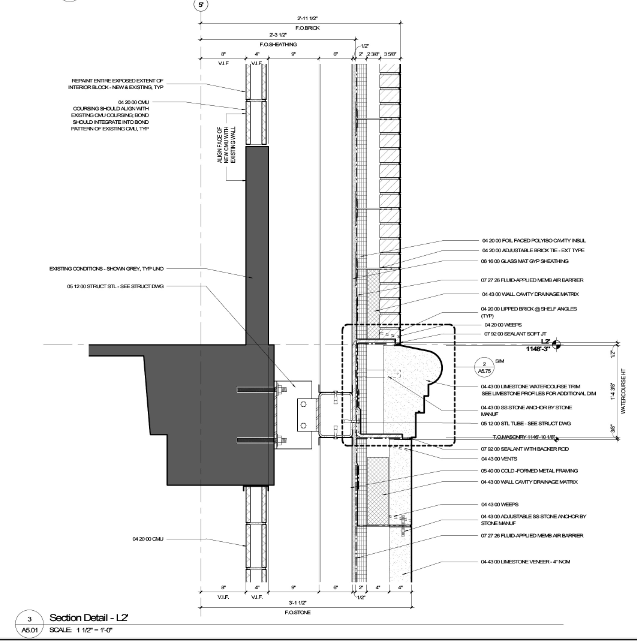 the Henderson North Building. A limestone trim will be used at the major building entrances, windowsills, wall caps, and trim. The punched windows in this exterior wall type will be aluminum windows with 1” insulated glass. the Henderson North Building. A limestone trim will be used at the major building entrances, windowsills, wall caps, and trim. The punched windows in this exterior wall type will be aluminum windows with 1” insulated glass.
Exterior glazed walls will also be utilized for the building enclosure. The typical glazed walls will be comprised of an aluminum wall system with a powder-coated finish. The glazing will be 1” thick insulated glass units.
One area of the building will include a prefinished composite metal panel system. This system will include an exterior air cavity with rigid insulation and a sheet membrane air/vapor barrier, dens-glass gypsum sheathing, galvanized metal studs and abuse resistant gypsum wallboard. The panels that will be used will be modular, smoothfaced panels with a powder-coated finish.
Figure 2 Typical Wall Section (BCJ)
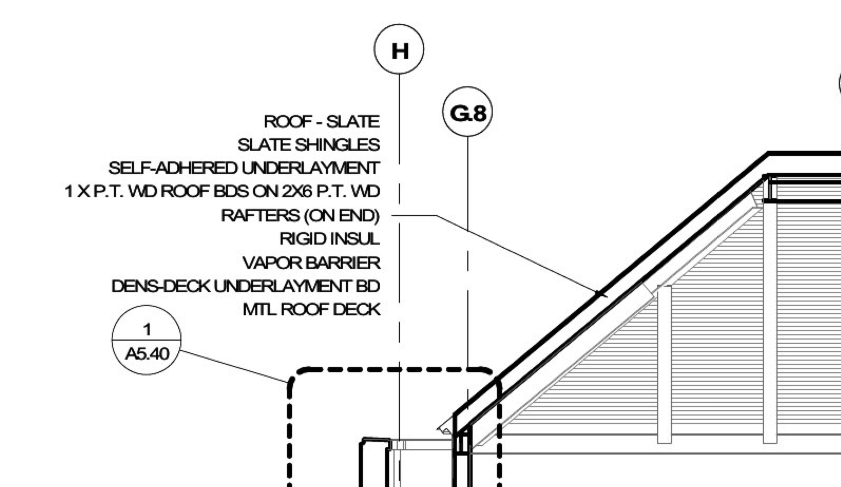 There are two different types of roofing that will be utilized on this project: a sloped roof and a flat (high) roof. The sloped roofs will be slate shingles on building paper, a vented nailable rigid insulation, vapor barrier, and dens-deck underlayment board on top of the structural roof deck. The flat (high) roof will be an adhered membrane roof (white) on dens-deck prime sheathing, rigidtapered polyisocyanurate board insulation, a vapor barrier, and dens-deck underlayment. There are two different types of roofing that will be utilized on this project: a sloped roof and a flat (high) roof. The sloped roofs will be slate shingles on building paper, a vented nailable rigid insulation, vapor barrier, and dens-deck underlayment board on top of the structural roof deck. The flat (high) roof will be an adhered membrane roof (white) on dens-deck prime sheathing, rigidtapered polyisocyanurate board insulation, a vapor barrier, and dens-deck underlayment.
Figure 3 Roofing Section (BCJ)
Sustainability Features
The Health and Human Development Building will be designed to achieve a LEED silver rating. Penn State University requires that all of their newly constructed buildings achieve at least a LEED certified rating. The design team plans to follow the mandatory performance criteria pertaining to LEED credits as set forth by the University as well as additional sustainability features. A few measures that are being taken to achieve LEED certification include the use of recycled materials, regional materials, and low-emitting materials.
Please Click on the following link to download Building Statistics Part 1
Structural
The Health and Human Development Building consists of 4 stories and a mechanical penthouse. The foundation is made up of a shallow strip and spread footings foundation system. Foundations walls are placed on top of the strip footings around the building. These footings range from 18” to 36” in thickness. There is also a mat foundation present for the stair tower areas, which is 24” thick. Normal weight concrete will be used for all footings and must have a minimum compressive 28-day strength of 4 ksi. A soil nail wall is used in the area connecting to the existing to remain section in order to contain the pressure for the excavation. It is recommended that the foundations sit on solid dolomite bedrock in order to reduce settlement.
The main super structure of the building consists of structural steel columns, beams, and flanges. Floors are composed of composite concrete floor slabs on metal decking, which are supported by wide flange beams. A 5” thick slab-on-grade is located on the ground floor. A wide variety of beams and girder sizes are used to support the office, lab, and classroom spaces. Column sizes range from 8x31s to 12x170s. The lateral force resisting system is a combination of braced frames and moment resisting connections.
Construction
The project is funded through the Department of General Services (DGS). With this type of project, it is required that multiple prime contractors be used. A design-bid-build type of contract with multiple primes is utilized. With this many primes, collaboration is very important Duel trailers have been added to the site in order to increase collaboration and allow for small issues to be resolved quickly. A challenge with this project is the location and size of the site. The building is being constructed alongside one of the busiest streets on the Penn State University campus. Also, the site is very small due to its proximity to the HUB lawn (a major student gathering area). The site was compressed in order to minimize the amount of space taken up on the HUB lawn. With the small site, it is important to establish lay down areas for material storage and also designate spaces for site traffic.
Safety is a major concern on the site. Adjacent buildings will be fully functional throughout the construction process. Also, the constant traffic of students throughout the campus will need to be managed for activities such as steel lifts and demolition. A temporary sidewalk was constructed in order to increase site area and allow for a safe swing radius for a crane. Also, traffic control personnel will be utilized at all times to have eyes on pedestrian traffic around the site entrance. The building is expected to be finished in June of 2015.
Mechanical
With the Health and Human Development building being located on the Penn State campus, it is able to be hooked into the steam and chilled water loops that run through the campus. The building will consist of 6 new air handling units in order to pump air throughout the building. There is also an existing AHU that will be salvaged and reused in the existing to remain section. The air handling units will be located on the roofs of both the ETR (existing to remain) and the new building. The air will then be cooled and heated using VAV boxes. Exhaust fans are located throughout the building in bathrooms and lab spaces as well.
Lighting
The HHD building consists of both fluorescent and LED lighting fixtures. With the push to have lights that do not require maintenance, LED lights are utilized a lot more, especially in the atrium space where changing of light bulbs would be difficult. Fluorescent lights are utilized mostly in more private spaces. Occupancy sensors are used throughout the building in order to control the lighting and reduce energy usage.
Electrical
Similar to the mechanical system, the electrical system is also tied into the campus power. The main distribution switchgear is a 1600 A, 480/277, 3-phase, 4-wire switchgear. This is then distributed to two switchboards, which stem out to sub-distribution panels.
Fire Protection
The building contains a sprinkler system that runs throughout the building. Beams and columns are designed to be fire resistant through spray on fireproofing. This foam allows for a 2-hour fire rating. Stair towers and elevator towers will consist of fully grouted CMU to allow for them to have a 2-hour rating as well.
Transportation
The HHD building contains two passenger elevators located in the center of the existing to remain building and the southwest side of the new construction. There are two main stair towers that service the new building and one main stairwell to service the existing to remain building. These are the main means of egress in case of a fire emergency. The atrium area is also made up of a detailed, open stair tower.
Please click on the following link to download Building Statistics Part 2 |

 One of the main features of this project is the large atrium that faces College Avenue. This atrium will act as a transition space as well as a gathering place for students and faculty. The remaining of the building interior is composed of classrooms, offices, and labs, which will be utilized for students and faculty of the college of Health and Human Development.
One of the main features of this project is the large atrium that faces College Avenue. This atrium will act as a transition space as well as a gathering place for students and faculty. The remaining of the building interior is composed of classrooms, offices, and labs, which will be utilized for students and faculty of the college of Health and Human Development.
 the Henderson North Building. A limestone trim will be used at the major building entrances, windowsills, wall caps, and trim. The punched windows in this exterior wall type will be aluminum windows with 1” insulated glass.
the Henderson North Building. A limestone trim will be used at the major building entrances, windowsills, wall caps, and trim. The punched windows in this exterior wall type will be aluminum windows with 1” insulated glass.  There are two different types of roofing that will be utilized on this project: a sloped roof and a flat (high) roof. The sloped roofs will be slate shingles on building paper, a vented nailable rigid insulation, vapor barrier, and dens-deck underlayment board on top of the structural roof deck. The flat (high) roof will be an adhered membrane roof (white) on dens-deck prime sheathing, rigidtapered polyisocyanurate board insulation, a vapor barrier, and dens-deck underlayment.
There are two different types of roofing that will be utilized on this project: a sloped roof and a flat (high) roof. The sloped roofs will be slate shingles on building paper, a vented nailable rigid insulation, vapor barrier, and dens-deck underlayment board on top of the structural roof deck. The flat (high) roof will be an adhered membrane roof (white) on dens-deck prime sheathing, rigidtapered polyisocyanurate board insulation, a vapor barrier, and dens-deck underlayment.